Proton Therapy for Esophageal Cancer
Minimize risk to heart and lungs with targeted esophageal cancer treatment
Radiation therapy can be an important part of the treatment plan for esophageal cancer. However, since the esophagus is located so close to the heart and lungs, traditional x-ray radiation can increase the risk of short- and long-term side effects. Too much radiation can cause damage, increasing your risk of developing heart disease or lung disease.
With proton therapy, it is possible to deliver a higher dose of radiation to the esophageal tumor, while minimizing the risk to the heart and lungs. Proton therapy offers an unmatched level of precision: it goes to the site of the tumor and stops. Targeting the tumor with a higher dose increases the likelihood that the treatment will be successful.
Proton therapy is a potential treatment option for plans that include surgery (operable) and those that do not (non-operable). It’s also safe to undergo proton therapy along with chemotherapy. Proton therapy may even be used if you have had prior radiation for esophageal cancer.
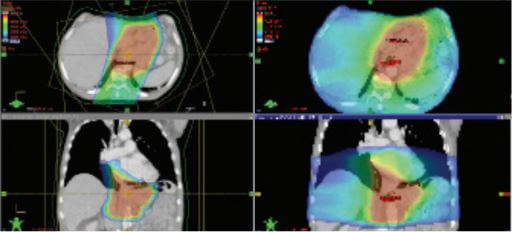
Comparison image – Proton Therapy is on the left, Photon Therapy is on the right
Esophageal cancers we treat with proton therapy
- Adenocarcinoma
- GE junction tumors
- Squamous cell carcinoma
Proton therapy for recurrent esophageal cancer
If you’ve previously had esophageal cancer and it was treated with radiation therapy, traditional x-ray radiation may not be recommended because the area around your tumor can only tolerate a limited amount of radiation over a lifetime. However, proton therapy can be safe to use for treating recurrent esophageal cancer, as it can provide an optimal dose of radiation to your tumor that limits the dose that the vital organs near the esophagus receive. This makes radiation a viable option for recurrent esophageal cancer.
Learn more about proton therapy
Request a consultation below to learn if proton therapy might benefit you. Our physicians will work with you and your care team to create your personalized treatment plan.